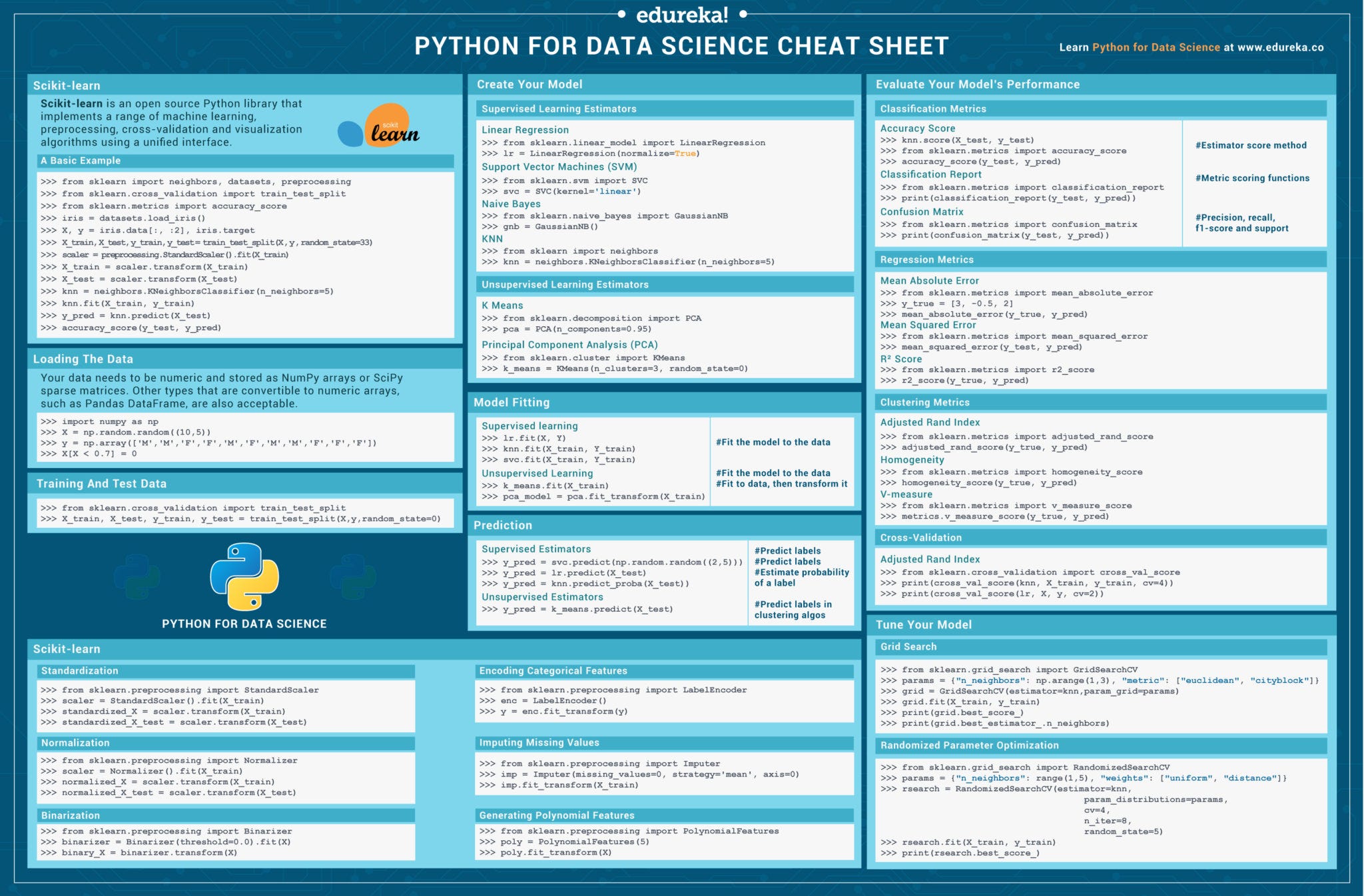
This is a summary of the models and metrics I learned in the Nanodegree Machine Learning Engineer from Udacity, in which I told my experience here. I added some models and libraries that I used at other times. As it is a quick chear sheet, the goal will always be to update this post.
Remember, this is not a post with details of each models or metrics, just to have a quick reminder, with brief summary of the model, advantages, disadvantages and examples of use cases. I put all the imports in the end, since we usually use more than one in one analysis.
Scikit-learn is an extremely useful library for various machine learning models. The sections above provided a basic step-by-step process to perform an analysis on different models. If you want to learn more however check out the documentation for Scikit-Learn, as. Keras Cheat Sheet (Datacamp) This 1-page cheat sheet is worth your time if you are looking into the specialized machine learning tool Keras. I have not yet used Keras myself but it is considered to be the best abstraction layer for deep learning and neural networks. Wikipedia defines Keras as follows.
- Supervised Learning
- Unsupervised Learning
Supervised Learning
Supervised Learning are Machine Learning models that based on historical data, with outputs that we already know as correct, the algorithm is trained to be able to predict new results.
There are two types of problems for this type of learning:
- Regression: we try to predict quantitative (numerical)
- Classification: we try to predict qualitative (discrete)
Naive Bayes
What is it?
It is a sort probabilíticos based on Bayes Theorem, created by Thomas Bayes. However, being naive it may have false positives.Bayes Theorem: probability of an event occurring conditioning the other.Example: A If the probability of happening B is happening XX%.
Naive: understand that all events are independent, which can generate false positives.
There are 3 types of classifiers Naives Bayes:
- Bernoulli Naive Bayes: will assume that the binary features are typically represented by 0 and 1 negative and positive.
- Multinomial Naive Bayes: used with the features are discretes, as words or classifications from 1 to 5.
Gaussian Naive Bayes: used when the features are continuous and there is the assumption of the normal distribution.
- Where can it be used?
- Spam filter
- Sentimental Analysis
- Profile analysis: a lending profile analysis, checks whether a user is a good payer, pays assiduously, among other variables, to complete the loan if it is profitable for that user
- Data Mining: database with various texts to identify literary author or style, based on the historical, such as text structure, language, words used
- There is a system that supports average decisions about cardiac disease, Heart Disease Prediction System. It was developed using as a main model the Naive Bayes. The model can answer complex queries to diagnose heart disease and thus help health professionals make intelligent clinical decisions than traditional systems of decision support can not * The model Gaussian Naives Bayes was used to predict inhibition of protein activity by small molecules absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion (ADME), prioritizing hit high throughput screening campaigns and enrichment of high yield coupling of the results
- Advantages
- Easy implementation
- Can work with categorical data and continuous
- It is performative and can be used in real time
- No need for a set of training data so large compared to other models
- Not to irrelevant features is sensitive
- Returns the degree of certainty of the answer
- Disadvantages
- Because it does not identify the interaction of the data, its dependence may occur false positives
- When dealing with phrases there is a problem it separate each word and there is loss of meaning as Chicago Bulls, with a basketball team and interpresta algorithm Chicago as a city and as Bulls as animal
Decision Trees
What is it?
Decision tree is a tree-shaped diagram used to determine a course of action. Each node of the tree represents a possible decision, occurrence or reaction.
A Decision Tree can be used in two ways:
- Classifier: used to predict values when the dependent variable (Y) is categorical.
Regression: used to predict values when the dependent variable (Y) is continuous.
- Where can it be used?
- Fraud Detection on credit cards, as can be seen in this example
- Recommendation Systems: like products, movies, websites, etc. A real case was Recommender Systems (RS), an algorithm created to increase sales and customer satisfaction. attempts to predict how a user will rank items based on their previous ratings and ratings from other users with similar profiles and thus recommend the item for purchase.
- Advantages
- Easy to understand, interpret and visualize
- Need little effort to prepare data (no need to normalize data, etc.)
- Can be used with categorical and numerical data
- No need to worry about outliers or if data is not linearly
- Easily read with feature interactions and not parametric
- Disadvantages
- Does not support online learning, needs to rebuild the tree when it gets new data
- It can be easily overfitting, however it can be resolved with Ensemble Methods
- The model may become unstable due to the small variation in the data
- Stability: small variations in the data can generate many different trees
- May be biased if some class is dominant
Support Vector Machines
What is it?
It can be used for classification and regression problems. It uses a technique called kernel to transform its data, and then, based on those transformations, it finds an optimal boundary between possible outputs.
- Where can it be used?
- Facial recognition
- Calligraphy Recognition
- Protein Structure Forecast
- Breast Cancer Diagnostics: experimental results show that linear kernel based on the bagging method may be the best choices for a small-scale dataset where the selection of features must be performed at the pre-processing stage of data .For a large-scale dataset, the RBF kernel based on the boosting method had better enhancement performance than the other classifiers, see this example
- Advantages
- High accuracy
- Can work with non-linear data
- Works well with data not yet structured and semi-structured, such as text, images and trees
- With an appropriate kernel function, you can solve complex problems
- Works well with high dimensional data
- Low risk of overfitting, using the correct kernels
- Disadvantages
- Does not provide probability estimates directly
- Does not perform well with large training data sets
- Difficult to choose a good kernel function
- Difficult to understand and interpret the final model, variable weights and individual impact.
Linear Regressions
Machine Learning Metrics Cheat Sheet Pdf
What is it?
Linear Regression is used to predict the continuous output indices (X). It has a linear relationship with the values of X to predict the value of Y.
- Simple Linear Regression: When there is only one input variable (X)
Multiple Linear Regression: When there are only two or more input variables (X)
- Can it be used?
- Forecast the annual time depending on the time of experience in a company
- Predict Sales x Amount invested for marketing
- Predict Daily Weight Gain vs. Input Weight
- Provide Acquisition of credit cards / Card limit, multiplus benefits
- Forecast Production vs. Quantity of Exports and Capacity
- Forecast Economic growth
- Advantages
- Easy to understand and explain
- Identification of the sensate the model edit textualized values (R²)
- Can work with a small dataset
- Disadvantages
- Requires an output variable to do the normal distribution
- Hardly R² is high for real cases
- Concepts
- SSE (Sum of Square Errors): Sum of Errors, Squares, Minimum, Used for Score of other models as fit metric
- Degree of freedom: Degrees of freedom, number of values in the final calculation of a statistic that are free to vary
- R²: a coefficient of determination that varies between 0 and 1 and shows the explanatory model of the observed values. The higher the R², the more explanatory the model is, the better it adjusts to the sample.
K-Nearest Neighbors
What is it?
Estimate the probability associated with the occurrence of a given event due to some features. The results of the analysis are contained within a range of 0 to 1.
- Where can it be used?
- Risk forecast the tax area
- Used to rank if the company is in the solvent or insolvent group of companies
- Determine what characteristics lead companies to adopt the balanced scorecard
- Advantages
- Provide result in terms of probability
- High degree of reliability
- It is not necessary to assume multicollinearity
- Models can be easily updated with new data
- Disadvantages
- Sensitive to outliers
- Does not perfom well with high dimensionality
Logistic Regression
What is it?
Algorithm that estimates the probability associated to the occurrence of a certain event due to some features. Its output variable needs to be continuous and discrete inputs.
- Where can it be used?
- Image Segmentation and Categorization
- Geographic Image Processing
- Handwriting recognition
- Spam detection
- Advantages
- Logistic models can be updated easily with new data
- It is not necessary to worry about multicollinearity of data * Besides being a classifier also returns probability, percentage of the event can occur or not
- Disadvantages
- Does not work well with outliers
- Does not work well with a large number of categorical variables
Ensemble Methods
What is it?
Ensemble methods are ways to combine multiple models, creating a stronger and more accurate model.
Some of the methods are:
- Random Florest: used to build a model based on multiple Decision Trees during the training phase.
- AdaBoost: improves the model by means of the errors, changing the weights.
- Bagging: trains into several subsets, ie separates training data and divides them randomly, each having a weak learner, then joins the results of the weak learner to create a model based on the outputs most viewed by the models
- Gradient Boosting: attempts to minimize the Mean Square Error (MSE), so long as the sum of the residuals is close to 0 (or minimum) and the predicted values are close enough to the actual values.
XGBoost (Extreme Gradient Boosting): is an advanced implementation of Gradient Boosting, yet faster and with high predictive power. It has a variety of regularizations that reduce overfitting and improve overall performance.
- Where can it be used?
- Random Florest used in Kinect to track body movements and recreate them in-game.
AdaBoosting was used to detect the analysis of baseball player games, see the documentation.
- Advantages
- Better at avoiding overfitting
- Usually has models with stronger predictive power and accuracy than single models
- Disadvantages
- Scaling: Generally by training multiple models, can perform poorly with large datasets
- Difficult to deploy on real-time platform
Evaluating Models
Acronyms used in the concepts below:
- TP: True Positive, values that were correctly predicted by the algorithm as positive
- FP: False Positive, values that were incorrectly predicted to be positive
- TN: True Negatives, values that were correctly predicted to be negative
FN: False Negatives, values that were incorrectly predicted to be negative
- Accuracy: measures how often the classifier makes the correct prediction. It is the ratio between the number of correct predictions and the total number of predictions (the number of records tested). Mathematically expressed by:
begin{align}dot{Acurácia} & = frac{TP+TN}{TP+TN+FP+FN} end{align}
- Confusion Matrix: is an array of real values and values predicted by its algorithm, showing how many TP, TN, FP, and FN its model got. As we can see in Figure 1:
- Precision: is the ratio of true positives to all positives, regardless of whether they are classified correctly or not. Mathematically represented by:
begin{align}dot{Precision} & = frac{TP}{TP+FP} end{align}
- Recall: also called True Positive Rate (TPR) or Sensitivity, is the ratio of True Positives to all positives correctly classified and false negatives. Mathematically represented by:
begin{align}dot{Recall} & = frac{TP}{TP+FN} end{align}
- ROC: traces TPR vs. FPR at different classification thresholds. Decreasing the classification threshold classifies more items as positive, thus increasing both false positives and true positives. In other words, a model predicts the probability of a class being 1 or 0, using these probabilities it is possible to plot a distribution graph as in figure bellow, with the red curve representing 0 and the green curve for 1, with 0.5 being the limit between two classes
All positive values above the limit (greater than 0.5) will be True Positives (TP), and all negative values above the limit will be False Positives (FP), since they were incorrectly classified as positive values. Below the limit, all negative values will be True Negatives (TN) and positive False Negatives (FN), since they were incorrectly classified as negative. This concept is best demonstrated in Figure 3.
- AUC: measures the entire two-dimensional area under any ROC curve. AUC provides an aggregate measure of performance in all possible classification limits. One way to interpret AUC is as the probability of the model classifying a random positive example more than a random negative example. A model whose predictions are 100% wrong has an AUC of 0.0; while one whose predictions are 100% correct has an AUC of 1.0. According to Figure 4.
Classification Report: it is a report table with the main evaluation metrics for each class, being:: recall, precision and f1_score.
f1_score: is the harmonic mean that considers both: precision and recall, its formula being expressed by:
begin{align}dot{f1 score} & = 2 cdot frac{precision cdot recall}{precision + recall} end{align}
- fbeta_score: calculated using the mean (harmonic) of the precision and recall values, having a beta parameter that determines the weight of the precision in the score, being
beta <1with greater weight for precision and ` beta> 1` favoring recall (beta = 0 consider only precision, beta = inf only recall). Mathematically expressed by:
begin{align}dot{F_beta score} = (1 + beta^2) cdot frac{precision cdot recall}{(beta^2 cdot precision) + recall}end{align}
Unupervised Learning
Unsupervised Learning are Machine Learning models that have little or none historical data to be based on and to predict results, they do not need a dataset to tell which are the correct output variables to model a predictive algorithm. These models can create data structures based on relationships between variables or detect some trends with clustering.
KMeans
What is it?
An algorithm that groups data that has characteristics similar to each other in a cluster. The K-means method has this name because K represents a number, since it is necessary to tell the algorithm how many clusters it wants to split the data. K-means is most commonly used in general use, with clusters of equal sizes, plane geometry, without large amounts of clusters. The algorithm always tries to find circular, spherical clusters.
It uses the distance measure to tell how similar each observation is, and can be:
- Euclidean distance: Euclidean distance between two points in a straight line
- Distance from Manhattan: sum of the distances between the lines that form 90º between two points, that is, sum of the line y to the point of intersection and line x. These measures are sensitive to the difference of scales between different variables:
Cosine distance: measure of the angle between two vectors. If the angle is 0 there is total similarity and if is π there is no relation between the objects.
- Where can it be used?
- Academic performance, based on student grades to separate students A, B or C
- Diagnostic system
- Movie catalog rating
- Classification of species of animals or plants
- Segmentation of customers according to consumption profiles
- Advantages
- Easy implementation and interpretation
- Good when you already have an idea of the required number of clusters
- Good scalability with many variables if k is not so high
- Disadvantages
- Early seeds have a great impact on the final results due to the local minumm when they are started in not so suitable places. Difficulty that can be bypassed by running the algorithm many times
- Difficult to predict the number of clusters (K-Value), you can use * elbow method * to get around this
- Sensitive to outliers
- Do not mess with missing values
- Does not work well with clusters that are not circular or spherical
- Sklearn Commands
- n_clusters: number of desired clusters, default 8
- max_iter: how many maximum interactions between assigning the points and moving the centroid, standard 300
- n_init: how many times the algorithm changes the centroids for different clusters, standard 10
- How to find the number of clusters (k)
- Elbow Method: method used to find the number of clusters most suitable for each data set, it plots the upstream values of k versus the total error calculated using this k. Here is a code to find this value:
Hierarchical
What is it?
The result of this algorithm is a grouping structure that gives us a visual indication of the relationship between clusters. It unified the data into clusters according to minimum distances, which are calculated according to each method:
Single Link: assumes that all points are a cluster and then groups them into clusters according to the distance of the points. Then, when there is an isolated point, it looks for the two ** closest points ** in the two clusters which is the distance between the clusters, and then joins the points forming another cluster. And then we choose how many clusters we want. This method does not exist in sklearn, instead we use Complete Link
Complete Link: assumes that all points are a cluster and then group them into clusters according to the distance of the points forming another cluster. And then, when there is an isolated point, it looks for the two most distant points in the two clusters which is the distance between the clusters, and then joins the points. And then we choose how many clusters we want.To join other clusters, it calculates the largest distance between the points, which we will name distance X, then measure the smallest distance X between clusters to join them.The problem of this method is that only one point is analyzed to verify the smallest distance, without taking into account the other data, which may be more dense, and may be another cluster.
Average Link: checks the distance between all points between clusters and the average of all distances is the distance measure between the two clusters.
Ward’s Link: method that attempts to minimize variance by merging the two clusters. It calculates a center point between two clusters, then checks the distance between each point and the center point, raises them squarely and sums all distances. Then it calculates a center point in each cluster, and subtracts each distance between points and center point of each cluster, raised to the square. ** This is the default sklean method. **
- Where can it be used?
- Using the Average Link method, it was possible to group produced proteins, used to create clusters of fungi types, see documentation
- Using the Complete Link method to draw a human microbiome diagram, see the documentation
- Advantages
- Works well with two-growing data set and two-rings
- Easy visualization of each clusters (dendograms)
- Especially powerful when the data set contains real hierarchical relationship (EX: evolutionary biology)
- Resulting hierarchical representations are very informative
- Disadvantages
- You need to choose which method is most appropriate
- Sensitive to noise and outilers
- It needs greater computational capacity when it has large datasets and many dimensionalities
Density Based Spatial Clustering of Application with Noise
What is it?
The algorithm groups the data that is dense together, points close together, and not all points are part of a cluster, the model names the other points as noise.It checks the distance ε (epsilon) around the points and if there are no other near enough points, it is considered noise. We have to set the parameters of minimum number of points per cluster and distance ε.Core point: is the point that has the minimum number of points required and identifies a cluster. The same cluster can have multiple core pointsBorder point: points that do not have the minimum number of required points around, yet are part of a cluster around a Core Point
- Where can it be used?
- Analyze network traffic, a network administrator can separate groups of traffic types as users of bulk downloads and others. See the documentation
- Detection of anomalies in temperature data, in which the points named as noises are anomalies, outliers. See the documentation
- Advantages
- Good with data set with noise or outliers
- Flexible to work with different forms and constraints of clusters
- It is not necessary to specify the number of clusters
- Works well with two-growing data set and two-rings
- Disadvantages
- Border points that can be accessed from two clusters are assigned to the cluster that first encounters it
- It faces difficulty in finding clusters of different densities, we can use HDBSCAN in these cases
Gaussian Mixture Models
What is it?
It is a lightweight clustering algorithm in which all data is part of all clusters, yet with different levels of belonging. It does a data distribution, and if it is Gaussian they have a higher clustering level, that is, it mixes the Gaussian distributions to separate the clusters.
It works by the Expectation Maximization algorithm in the following steps:
- Define K, number Gaussian distributions. Mean setar and variances
- Step E, smooth grouping of the data. calculates the degree of ownership of each point for each cluster
- Step M, maximization step, use the data from the previous step and create new mean and variance parameters for each cluster. in a weighted way taking into account the level of ownership of each point
Validate the log-likelihood (log-likelihood) to check if it converges. The higher the number, the more certain we have that the mix model we generate is responsible for creating the data or fitting into the dataset we have
- Where can it be used?
- Reading sensor data to find people routines. Ex: As a shift sensor, the algorithm can identify when they are in the office, dining or out. Or, it can differentiate the way of driving that the person used. See the documentation
- Identify speech, signatures, biometrics.
- Computer vision, can detect image backgrounds, for example taking people out of a video and leaving just the scenery. See the documentation
- Advantages
- Needs less training than other models, such as logistic regression
- High scalability
- Not sensitive to * features * with little importance
- Returns the degree of certainty of the answer
- Light clustering, which makes samples part of multiple clusters
- Disadvantages
- Sensitive to initialization values
- The convergence rate is slow
- It is not good to learn with interactions of features, for example, if you like ice cream of flakes and chocolate, but hate the two flavors together
- Sensitive to initialization values
Evaluating Models
External Indices: used when the original data is labeled. One of its indexes is the Adjusted Rand score, being -1 to 1, the higher the better.
Internal Indices: used to request the adjustment between the data and the structure. One of its indexes is the Silhouette score, being -1 to 1, the higher the better, it is not a good index for DBSCAN, nor is it for clusters defined as two-rings. Good for compact, dense, circular groupings. For DBSCAN it is good to use the DBCV index.
Relative Indices: indicates which cluster structure is best in some sense
Validation indices are defined as:
- Compression: measure of proximity of the elements in each group
- Separability: measure of how far the clusters are from each other
Feature Scaling
What is it?
Method for transforming features with similar ranges so that they can be computable, usually between 0 and 1.In Sklearn there is a method that does this, MinMaxScaler, which transforms the data in this scale, but it must remember that your array must have numbers float (decimals)
Examples of templates that are affected by Feature Scaling:
- K-Means
- SVM with RBF
Examples of models that are not ** affected by Feature Scaling:
- Lienar Regression
Decision Trees
- Advantages
- Have a reliable number compared to what you expect on the way out
- Disadvantages
- Sensitive to outilers
Principal Component Analysis
What is it?
- Used to reduce the dimensionality of the features by maximizing the variances, losing the least amount of information to the designer data
- PCA is a systematized model of transforming the features of inputs into main components.
- These Main Components are available for use in place of the original features
- You can rank the Main Components
- The Main Components must be perpendicular to each other (90º), which means that they are independent of each other
- The maximum number of Main Components that can be obtained is equal to the number of inputs of the data set, however it is advisable not to use all, but those with the highest raking
Measurable variables: can measure directly, such as m², number of rooms, school ranking
Latent variables: we can not measure directly, but it is represented by other indicators (the measurable ones), generating a theoretical sense. Ex: size is the latent variable and its measurable variables are m² and number of rooms.
- When to use?
- When we want to see whether latent variables that can be shown in the data patterns
- Decrease dimensionality to:
- View when we have large dimensionaldiades
- Decrease noise
- Pre-processing the data
- Where can it be used?
- Facial recognition along with SVM

Random Projection
Python Machine Learning Cheat Sheet
- What is it?
A dimensionality reduction method, mathematically more efficient and perfomatic than PCA for working with a large dimensional data set. Based on the Johnson-Linderstrauss Lemma, the algorithm multiplies the data set by a random matrix, preserving the distances between the points to a large degree, causing the number of dimensions to decrease
Independent Component Analysis
What is it?
ICA assumes that features are mixtures of independent sources, and the algorithm tries to isolate them from each other.A well-known example is the “Party Problem” which shows three people in the same hall in different locations, each recording the sound of the venue. Each venue is playing something different such as piano, cello guitar, and a TV.
All recordings pick up the sounds, but of different intensity for each. Clearing the three recordings to get the sound of each object alone is what the ICA does, and this process is called Blind source separationThe algorithm assumes that the components are statistically independent and with a non-Gaussian distribution
- Where can it be used?
- Medical Scanners: Brain mapping, sensors detect electrical or magnetic signals. ICA can be used to find the independent components within the brain.
- Magnetic resonance imaging to isolate where each signal from the brain comes from
Importing libraries
Bibliography
Castle, Nikki. 2017. Supervised vs. Unsupervised Machine Learning
Çelik, Mete, et al. 2001.Anomaly detection in temperature data using DBSCAN algorithm
Chen, Edwin. Choosing a Machine Learning Classifier
Erman, Jefreey, et al. 2006. Traffic Classification Using Clustering Algorithms
Gershman, Amir, et al. A Decision Tree Based Recommender System
Grover, Prince. 2017. Gradient Boosting from scratch
Huang, Min-Wei, et al. 2017. SVM and SVM Ensembles in Breast CancerPrediction
Klon, Anthony E., et al 2006. Improved Naive Bayesian Modeling of Numerical Data for Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism and Excretion (ADME) Property Prediction
Markoski,Branko. 2015. Application of AdaBoost Algorithm inBasketball Player Detection
Pattekari,Shadab Adam & Parveen, Asma. 2012. PREDICTION SYSTEM FOR HEART DISEASE USING NAIVE BAYES
Portella, Letícia. 2018. Machine Learning Models - My Cheat List
Sachanm Lalit, 2015. Logistic Regression vs Decision Trees vs SVM: Part II
Saunders, Diane, et al. 2012. Using hierarchical clustering of secreted protein families to classify and rank candidate effectors of rust fungi
Simplilean. 2018. Naive Bayes Classifier
Azure Machine Learning Cheat Sheet
Simplilean. 2018. KNN Algorithm
Singh, Aishwarya. 2018. A Comprehensive Guide to Ensemble Learning (with Python codes)
Sonagara, Darshan and Badheka, Soham. 2014. Comparison of Basic Clustering Algorithms
Spencer, Melanie, et al. 2010. Association between composition of the human gastrointestinal microbiome and development of fatty liver with choline deficiency
Machine Learning Metrics Cheat Sheet
Statinfer, 2017. SVM : Advantages Disadvantages and Applications
Stauffer, Chris and Grmson W, E, L. Adaptive background mixture models for real-time tracking
Machine Learning Models Cheat Sheet
Sun, Feng-Tso, et al. Nonparametric Discovery of Human Routines from Sensor Data
